论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.00596
知乎翻译:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/538914712
https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs224w/index.html
论文
recurrent graph neural networks
convolutional graph neural networks
graph autoencoders
spatial-temporal graph neural networks 时空图神经网络
第二节 背景
第三节 分类
第四-七节 概述模型
第八节 应用
第九节 未来
图的不同处理方式:
graph kernel methods
处理图分类时,通过核方法(kernel)测量图对的相似性。然后支持向量机就可以起到作用了。
These methods employ a kernel function to measure the similarity between pairs of graphs so that kernel-based algorithms like support vector machines can be used for supervised learning on graphs.
graph kernel同样是将nodes映射到向量空间。但是这个映射函数是确定的。
Graph neural networks
define
- Spatial-Temporal Graph
A spatial-temporal graph is an attributed graph where the node attributes change dynamically over time. The spatial-temporal graph is defined as G(t) = (V, E,X(t)) with X(t) ∈ Rn×d. 节点属性随时间变化的图
模型分类
Taxonomy of Graph Neural Networks
- recurrent graph neural networks
在GNN里面加入GRU等RNN模型来传递基于时间的消息。
- convolutional graph neural networks
分为基础图谱理论的卷积(GCN)和空间卷积(GAT不确定)
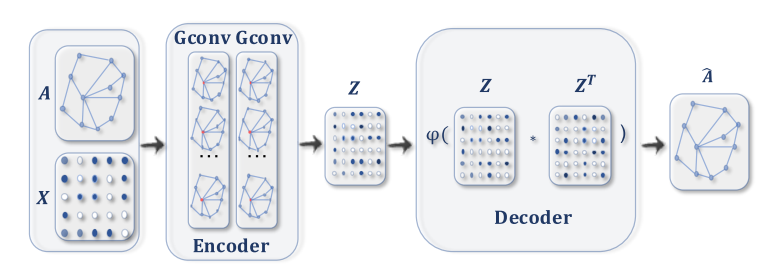
- graph autoencoders GAE
encode nodes/graphs into a latent vector space and reconstruct graph data from the encoded information.
encode nodes/graphs 到潜在的向量空间(有没有可能能称为特征空间),然后根据encode的信息来重构图数据。
这是一个unsupervised learning的模型,可以实现图聚类等任务
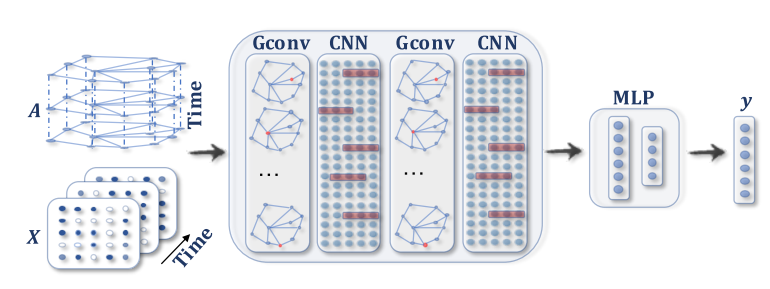
- spatial-temporal graph neural networks STGNN 时空图神经网络
完成人类动作识别(human action recognition)等任务,处理的是spatial-temporal graphs(时空图)
The key idea of STGNNs is to consider spatial dependency and temporal dependency at the same time.
STGNNs 同时考虑空间和时间
Many current approaches integrate graph convolutions to capture spatial dependency with RNNs or CNNs to model the temporal dependency.
integrate 合并;成为一体
Frameworks
- outputs relate to node regression and node classification tasks.
- outputs relate to the edge classification and link prediction tasks.
- outputs relate to the graph classification task.
Training Frameworks
- Semi-supervised learning for node-level classification 半监督学习的node-level分类(GCN)比如Cora数据集。
- Supervised learning for graph-level classification 监督学习的图分类
- Unsupervised learning for graph embedding 无监督学习的图嵌入
只有边信息没有点信息时,看的很模糊
RECURRENT GRAPH NEURAL NETWORKS RecGNNs
Readout
Readout函数是用来将节点的特征聚合起来
They apply the same set of parameters recurrently over nodes in a graph to extract high-level node representations.
对图的每个节点使用相同的一组参数来抽取节点特征。
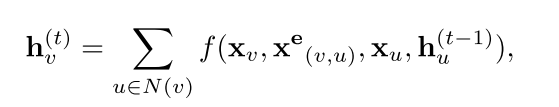
GGNN
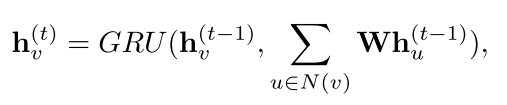
这里注意是使用的循环而不是时序。定义 \[ h_v^0=x_v \] 但是在使用时间反向传播(BPTT)时不好处理。
下图是原论文中The basic recurrence of the propagation model is
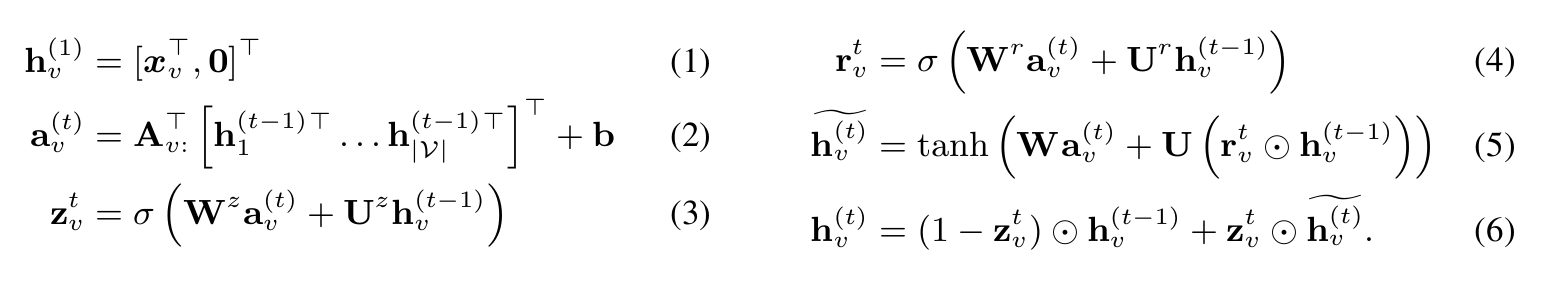
未完成
CONVOLUTIONAL GRAPH NEURAL NETWORKS GCN
Spectral-based ConvGNNs
normalized graph Laplacian matrix是一个实对称半正定矩阵 \[ L = I_n-D^{-1/2}AD^{-1/2} \\ 分解为 L=UΛU^T,U=[u_0,u_1,....,u_{n-1}] \\ 且UU^T=I \\ 定义graph\ Fourier\ transform:f(X)=U^TX \\ inverse graph Fourier transform: f^{-1}(\hat X)=U\hat X \] The graph Fourier transform projects the input graph signal to the orthonormal space where the basis is formed by eigenvectors of the normalized graph Laplacian.
orthonormal space 正交空间
Elements of the transformed signal x hat are the coordinates of the graph signal in the new space so that the input signal can be represented as \[ x =\sum_{i}{\hat x_iu_i} \]
which is exactly the inverse graph Fourier transform.
即x hat 是x在正交空间的坐标。为什么x hat的在正交基下的坐标为 \[
\hat x = [u_0^Tx, u_1^Tx,...,u_{n-1}^Tx]\\
\] 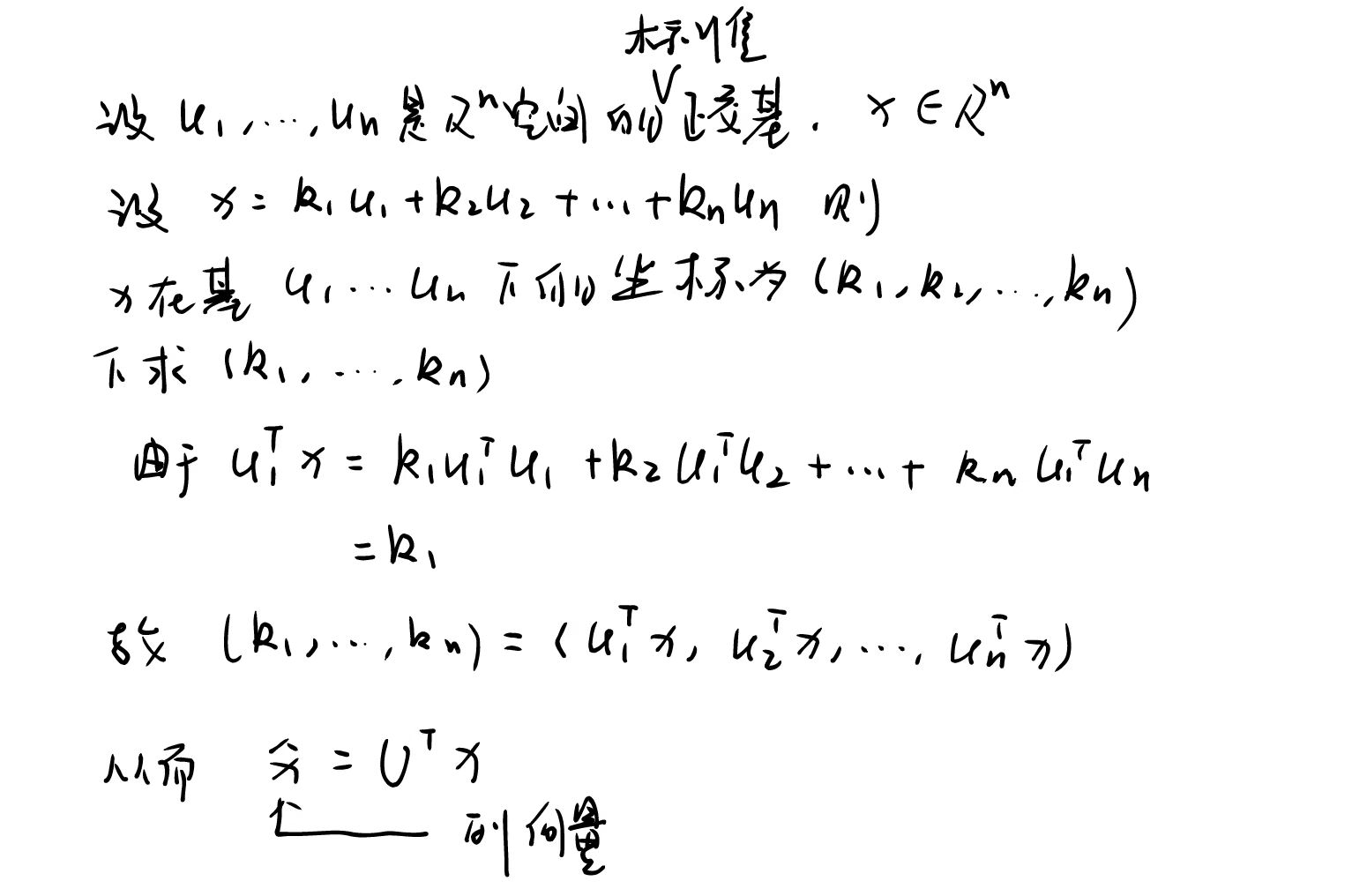

上图解释了谱域卷积的定义,不同的模型对应不同的gθ.
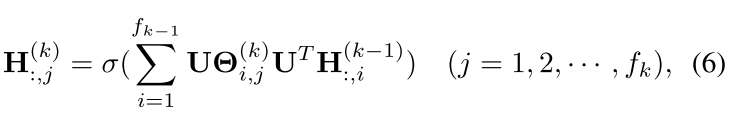
隐藏层的传递如上图。相当于是在做特征融合。和MLP类似。这样定义的θ将会是一个三维张量。第一个维度代表它的channels
原文:θ(i,j) is a diagonal matrix filled with learnable parameters.即是一个对角矩阵
在GCN中θ(i,j)会是一个标量。
GCN

上图有一些错误:
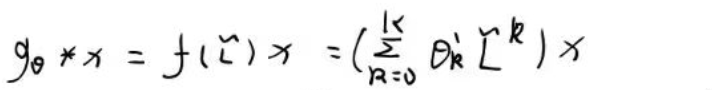
应该是: \[ =\sum_{k=o}^Kθ_k^,T_k(\hat L) \\ 当取K=1是,依然是与上图相同的结果 \]
观察GCN的θ(i,j)=θΛ,参数减少了很多。这里也是一个有意思的点!
缺点:
Due to the eigen-decomposition of the Laplacian matrix, Spectral CNN faces three limitations. First, any perturbation to a graph results in a change of eigenbasis. Second, the learned filters are domain dependent, meaning they cannot be applied to a graph with a different structure.
- 图的结构变动会导致基的变化
- 不能用于具有不同图结构的数据集