transformer结束后开始学习图神经网络了。
看了GCN的论文,下面从使用与模型背后的数学原理分别介绍。
处理的数据集是Cora数据集,即半监督学习的分类问题,最后精度和论文差不多。
# 直接使用 GCN的隐藏层传递公式如下: 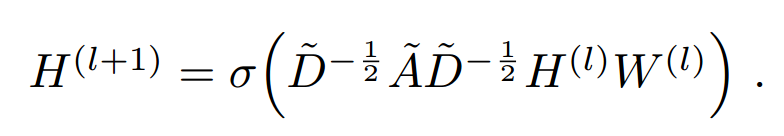
其中DAD这一堆东西是可以从图的结构(即邻接矩阵)直接给出的。\(H^0=X,X=(x_1,x_2,...,x_c),x_i是图的第i个节点的特征向量。W=(w_1,...,w_f)是需要拟合的参数,f代表通道数(channels)(和CNN的通道数相似),w_i是一个过滤器(filter)\)
层传递公式就是这样,下面用pyg实现: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch_geometric import nn
from torch_geometric.data import Data
from torch_geometric.datasets import Planetoid
class GCN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, hidden_channels, num_classify, dropout):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.GCNConv(in_channels, hidden_channels)
self.conv2 = nn.GCNConv(hidden_channels, num_classify)
self.dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, graph):
x,edge_index = graph.x, graph.edge_index
h = F.relu(self.conv1(x,edge_index))
if self.training:
h = self.dropout(h)
o = self.conv2(h,edge_index)
return o
def test_accuracy(net, cora_data):
net.eval()
out = net(cora_data)
test_outs = out[cora_data.test_mask].argmax(dim=1)
test_labels = cora_data.y[cora_data.test_mask]
score = test_outs[test_outs==test_labels].shape[0]/test_outs.shape[0]
return score
dataset = Planetoid(root='./data/Cora', name='Cora')
cora_data = dataset[0]
hidden_channels = 32
epochs, lr = 200, 0.01
weight_decay = 5e-4
net = GCN(cora_data.num_features, hidden_channels, dataset.num_classes, 0.2)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=weight_decay)
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
device = torch.device('cuda')
net = net.to(device)
cora_data = cora_data.to(device)
for e in range(epochs):
y_hat = net(cora_data)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = loss_fn(y_hat[cora_data.train_mask], cora_data.y[cora_data.train_mask])
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(f'epoch:{e}, loss:{loss.item()}')
print(test_accuracy(net, cora_data))
从零实现GCN网络
1 | import torch |
输出精度为0.832
数学原理
参考链接
数学分析之投影内积和傅里叶级数
GCN原理(写的很好!)
Graph Neural
Network (2/2) (由助教姜成翰同學講授)
【双语字幕】斯坦福CS224W《图机器学习》课程(2021)
by Jure Leskovec
「珂学原理」No.
26「拉普拉斯变换了什么?」
纯干货数学推导_傅里叶级数与傅里叶变换
B站首发!草履虫都能看懂的【傅里叶变换】讲解,清华大学李永乐老师教你如何理解...
## 个人理解 pass
原文的一些备注
diag(x),x is vector.将向量x对角化。
sys normalized laplacian matrix

图论的一个定理

Chebyshev Polynomial(切比雪夫多项式)
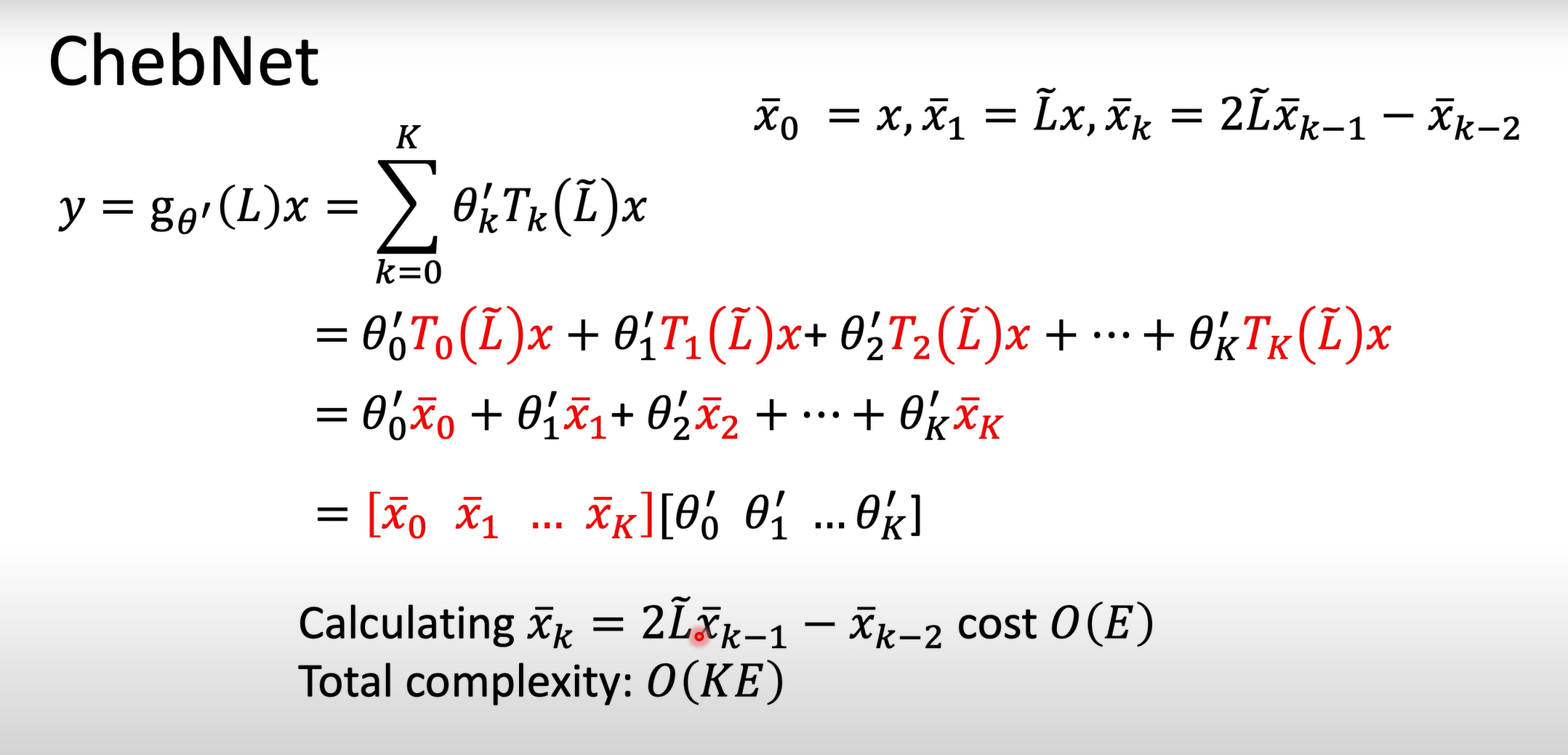
GCN对Fourier domain的变体
