RNN(循环神经网络,Recurrent Neural Network)是一类用于处理序列数据的神经网络模型。与传统的前馈神经网络不同,RNN具有记忆功能,可以捕捉序列数据中的时间依赖关系。这种能力使得RNN在处理语言、音频、时间序列等任务时非常有效。
RNN的关键特点是它们包含循环结构,允许信息在网络内传递。每个时间步,RNN接收输入并产生输出,同时在内部保留一个隐藏状态(hidden state)。这个隐藏状态包含了网络在之前的时间步中学到的信息,使得网络能够记忆先前的输入。
然而,传统的RNN在训练长序列时存在一些问题,例如梯度消失和梯度爆炸。为了解决这些问题,出现了一些改进型的循环神经网络,如长短时记忆网络(LSTM)和门控循环单元(GRU)。
个人理解RNN相当于是在MLP的网络结构上添加了上一个隐藏层到当前隐藏层的参数W,而这个W相当于抽象了输入序列\(X=(x_1,
x_2,...,x_n)\)的位置关系,使RNN具有记忆能力。
1.但是由于参数只有一个W,参数量不够。当n变大时,RNN对\(x_1,x_2...\)的权重会相对降低,但有时候\(x_1,x_2\)对X而言很重要。
2.在做反向传播的时候,根据公式推导,RNN比较容易出现梯度消失与梯度爆炸。
而GRU与LSTM就改进了RNN的这些问题。
问题:文本生成
训练集为timemachine小说,下面为部分截取: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16The Time Traveller (for so it will be convenient to speak of him)
was expounding a recondite matter to us. His grey eyes shone and
twinkled, and his usually pale face was flushed and animated. The
fire burned brightly, and the soft radiance of the incandescent
lights in the lilies of silver caught the bubbles that flashed and
passed in our glasses. Our chairs, being his patents, embraced and
caressed us rather than submitted to be sat upon, and there was that
luxurious after-dinner atmosphere when thought roams gracefully
free of the trammels of precision. And he put it to us in this
way--marking the points with a lean forefinger--as we sat and lazily
admired his earnestness over this new paradox (as we thought it)
and his fecundity.
'You must follow me carefully. I shall have to controvert one or two
ideas that are almost universally accepted. The geometry, for
instance, they taught you at school is founded on a misconception.'
模型评估标准
Perplexity( 困惑度)
Perplexity是一种用于评估语言模型性能的指标。它主要用于衡量一个语言模型在给定数据集上的预测效果,尤其是在文本生成任务中。
给定一个语言模型和一个文本序列,Perplexity的计算方式为:
\[ \text{Perplexity} = \exp\left(-\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} \log P(x_i)\right) \]
其中: - N是序列的长度。 - \(x_i\)是序列中的第i个词。 - \(p(x_i)\)是模型预测的第i个词的概率。
\(p(x_i)\)计算方法在模型定义后解释。
当\(p(x_i)趋近于1时,\left(-\frac{1}{N}
\sum_{i=1}^{N} \log
P(x_i)\right)趋近于0,Perplexity就趋近于1\)
当\(p(x_i)趋近于0时,\left(-\frac{1}{N}
\sum_{i=1}^{N} \log
P(x_i)\right)趋近于+\infty,Perplexity就趋近于+\infty\)
Perplexity越低,表示模型在给定的数据上的性能越好。一个完美的语言模型在给定数据上的Perplexity为1,因为它完全理解并能够准确地预测每个词。
# 循环神经网络模型(RNN) 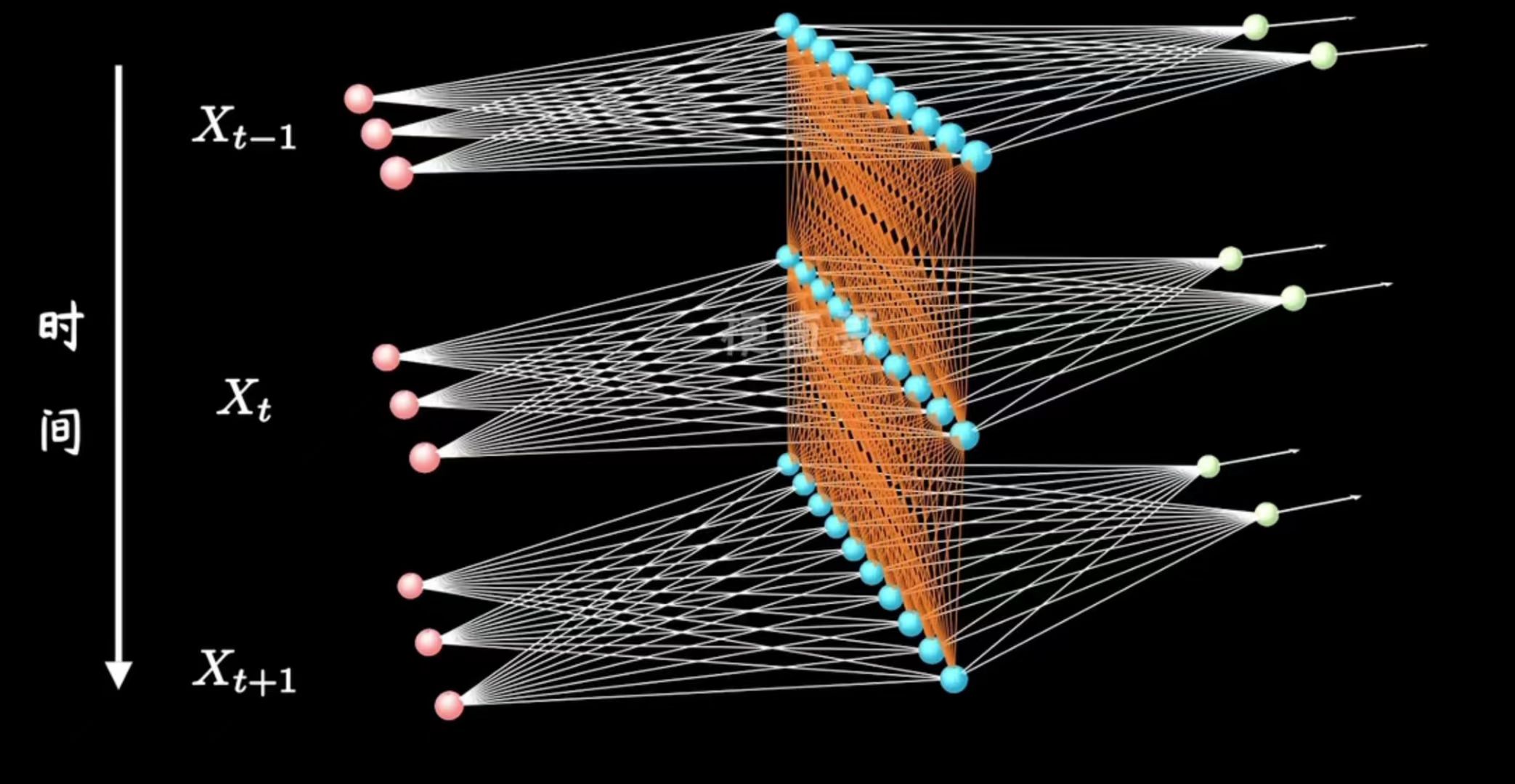 RNN是MLP的一个变体,简单的说,即在MLP的隐藏层上添加了输入,且输入的是上一个时间点的隐藏层数据。显然第一个时间点的隐藏层的输入是需要手动初始化的。
RNN是MLP的一个变体,简单的说,即在MLP的隐藏层上添加了输入,且输入的是上一个时间点的隐藏层数据。显然第一个时间点的隐藏层的输入是需要手动初始化的。
单隐藏层的RNN,计算公式如下:
\[
H^t=\sigma(W_{xh}X+W_{hh}H^{t-1}+b_h) \\\\
O = W_{ho}H^t+b_o
\] 需要拟合的参数为:\(W_{xh},W_{hh},W_{ho},b_h,b_o\)
例如:X是一个28维向量,H是一个64维向量,O是一个28维向量。则:
- \(W_{xh}\)是一个64x28的矩阵。
- \(W_{hh}\)是一个64x64的矩阵。
- \(W_{ho}\)是一个28x64的矩阵。
- \(b_h\)是一个64维的向量。
- \(b_o\)是一个28维的向量。
激活函数同样选择ReLU。
小说数据处理
由于数据是文本,所以需要对它进行建模处理,简单的实现是使用one-hot编码,由于是英文小说,字母数为26,将标点符号之类归为一类,再将序列开始与结束归为一类。那么一个字母one-hot编码后是一个28维的向量。
损失函数
模型的输出O是一个28维的向量,再将这个向量通过Softmax函数将其转化为概率分布。这样每一个分量分别表示对字母或符号的预测概率。上文中的\(P(x_i)\)就是这样计算。
这样其实就对应了一个分类问题,那么我们模型的损失函数可以使用交叉熵损失函数(Cross-Entropy
Loss) \[
\text{CrossEntropyLoss}=-\sum_{i=1}^{C} y_i\log(p_i)
\]
完整公式
\[ 计算全部损失:C = \frac{\sum_{i=1}^{T} c_i}{T} \\\\ 计算t时间步损失:c_t = -\sum_{i=1}^{N} y_i\log(p_t(i)) \\\\ t时间步Softmax的输出:p_t=\text{Softmax}(o_t) = \frac{e^{o_t(i)}}{\sum_{j=1}^{N} e^{o_t(j)}} \\\\ t时间步RNN的输出:o_t = W_{ho}h_t+b_o \\\\ t时间步RNN的隐藏层:h_t=\sigma(W_{xh}x+W_{hh}h_{t-1}+b_h) \\\\ \]
优化器
使用SGD。
训练模型
注意state.detach(),否则pytorch的计算图会报错。 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
from torch.nn import functional as F
batch_size = 32
vocab_size = 35
epochs, lr = 2000, 1
train_iter, vocab = d2l.load_data_time_machine(batch_size, vocab_size)
test_iter,_ = d2l.load_data_time_machine(1, vocab_size)
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs) -> None:
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=28, hidden_size=64, num_layers=1,nonlinearity='relu')
self.l = nn.Linear(64,28)
def forward(self, x, state):
x = F.one_hot(x.T,28).type(torch.float32)
h,state = self.rnn(x,state)
o = self.l(h.reshape(-1,64))
return o, state
net = RNN()
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
updater = torch.optim.SGD(params=net.parameters(),lr=lr)
state = torch.zeros((1,32,64), dtype=torch.float32)
device = torch.device('cuda')
net.to(device)
state = state.to(device)
for e in range(epochs):
for x,y in train_iter:
x,y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
state = state.detach()
y_hat,state = net(x,state)
# 计算loss展平
y = y.T.reshape(-1)
updater.zero_grad()
loss = loss_fn(y_hat, y.long())
loss.backward()
updater.step()
if e%100 == 0:
print('Perplexity: ', loss.item())
# Perplexity: 1.1171027421951294
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15def predict(prefix, num_preds, net, vocab, device):
state = torch.zeros((1,1,64), dtype=torch.float32).to(device)
outputs = [vocab[prefix[0]]]
get_input = lambda: torch.tensor([outputs[-1]], device=device).reshape((1, 1))
for y in prefix[1:]:
_,state = net(get_input(), state)
outputs.append(vocab[y])
for _ in range(num_preds): # 预测num_preds步
y, state = net(get_input(), state)
outputs.append(int(y.argmax(dim=1).reshape(1)))
return ''.join([vocab.idx_to_token[i] for i in outputs])
predict('time traveller', 100, net, vocab, device)
# 'time traveller and and the moment with a contere and the modelter dine they they that said the medical mant over a'
GRU的改进
对比RNN,GRU隐藏层的计算方式有所变化,GRU的更新公式如下: 
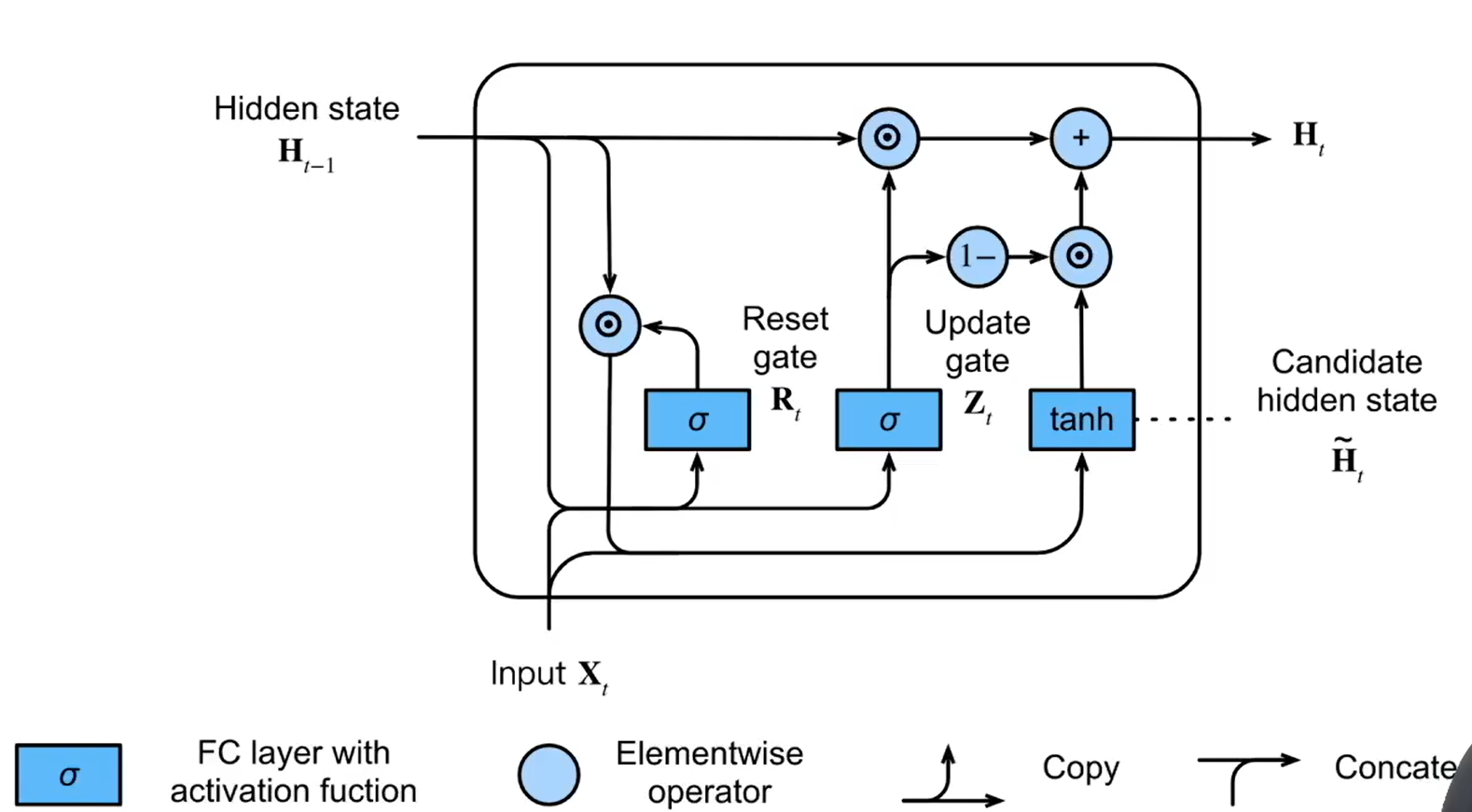 GRU先生成了两个特征,\(z_t\)和\(r_t\)这两个特征都是与隐藏层\(h\)同维度的向量。这两个特征的输入都是相同的但参数不同,相当于说GRU从输入中学到了两个不同的特征,对输入序列\(X=(x_1, x_2,...,x_n)\)而言,特征\(r_t\)表示来自过去的信息\(x_{1},x_{2},...x_{t-1}\)对\(x_{t}\)的重要程度,特征\(z_t\)表示当前步输入对序列的重要性。
GRU先生成了两个特征,\(z_t\)和\(r_t\)这两个特征都是与隐藏层\(h\)同维度的向量。这两个特征的输入都是相同的但参数不同,相当于说GRU从输入中学到了两个不同的特征,对输入序列\(X=(x_1, x_2,...,x_n)\)而言,特征\(r_t\)表示来自过去的信息\(x_{1},x_{2},...x_{t-1}\)对\(x_{t}\)的重要程度,特征\(z_t\)表示当前步输入对序列的重要性。