权重衰减
增加L2范数惩罚,使参数w足够小,防止过拟合。 \(L(w,b)+(\lambda/2)||w||^2\)
Dropout
Net定义
1 | def dropout_layer(x, dropout): |
多项式拟合
生成多项式数据
随机生成0-1均匀分布的数据,因为选择激活函数为RELU所以不能有负数的y,然后产生多项式,由于使用多层感知机,所以效果会比线性模型好很多,所以加大多项式次数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
import math
from torch.utils import data
from d2l.torch import Animator, Accumulator
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms
def get_polynomial_data(w, size=1000, max_degree=20):
true_w = np.zeros(max_degree)
true_w[:len(w)] = w
x = np.random.random(size=(size, 1))
np.random.shuffle(x)
# 生成多项式矩阵,行为1-20次方
input_x = np.power(x, np.arange(max_degree))
for i in range(max_degree):
input_x[:,i] /= math.gamma(i+1)
y = input_x.dot(true_w.reshape(-1,1)) + np.random.normal(scale=0.1, size=(input_x.shape[0],1))
input_x, y = [torch.tensor(data, dtype=torch.float32) for data in [input_x, y]]
return input_x, y
# len 8
w = [5, 1.2, 3.4, 5.6, 1.2, 2.5, 6.3, 0.1]
polydata, label = get_polynomial_data(w)
test_data, test_label = get_polynomial_data(w)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34def train(polydata, label, input_dim, test_data, test_label):
def init_weights(m):
if type == nn.Linear:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01)
# 开始时lr=0.1产生了爆炸
lr = 0.001
num_epochs = 10
batch_size = 100
train_set = data.TensorDataset(polydata[:,:input_dim], label)
train_iter = data.DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
net = Net(input_dim, 8, 8, 1, 0.5)
# net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_dim, 1))
net.apply(init_weights)
loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')
updater = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0, 2], legend=['train loss', 'test loss'])
for i in range(num_epochs):
metrics = Accumulator(2)
for x,y in train_iter:
y_hat = net(x)
l = loss(y_hat.reshape(y.shape), y)
metrics.add(float(l.sum()), y.numel())
updater.zero_grad()
l.sum().backward()
updater.step()
test_loss = loss(net(test_data[:,:input_dim]), test_label).mean().detach().numpy()
print(metrics[0], metrics[1], test_loss)
animator.add(i + 1, (metrics[0]/metrics[1], test_loss))
return net
net = train(polydata, label, 4, test_data, test_label)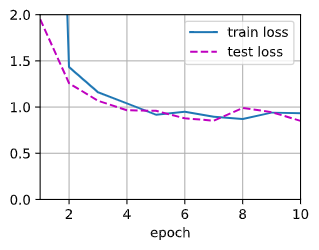 net =
nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_dim, 1))
net =
nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(input_dim, 1)) 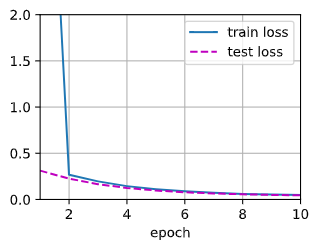 效果没有线性拟合好!
效果没有线性拟合好!
FashionMNIST
1 | from d2l import torch as d2l |
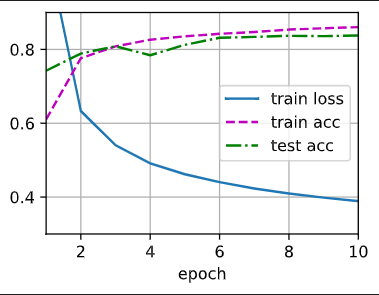 对比[多层感知机及代码实现Pytorch
d2l]中的图,可以看出过拟合的情况有所改善,而且这里的test
acc实在is_training=True的情况下,在真实预测的情况下可能会更好。
对比[多层感知机及代码实现Pytorch
d2l]中的图,可以看出过拟合的情况有所改善,而且这里的test
acc实在is_training=True的情况下,在真实预测的情况下可能会更好。