简介
1 | 在机器学习中,支持向量机(英语:support vector machine,常简称为SVM,又名支持向量网络[1])是在分类与回归分析中分析数据的监督式学习模型与相关的学习算法。 |
之下的总结顺序皆来自Andrew Ng
我的理解
对于我个人的理解,这是一个尝试实现将新输入的数据分类的算法。 即预先准备标记点
\[ \begin{bmatrix} f_1\\ f_2\\ {\vdots}\\ f_n\\ \end{bmatrix} \]
对于一个新输入的数据\(x_1\)。 \(x_1\)经过核函数处理后,得到f矩阵
\[ \begin{bmatrix} f_1^1\\ f_2^1\\ {\vdots}\\ f_n^1\\ \end{bmatrix} \]
后带入相似度函数
\[ h_{\theta}=\theta_{0}+\theta_{1}*f_{1}+\theta_{2}*f_{2}+...+\theta_{n}*f_{n} \]
得到值后根据值是否大于0进行分类。 然后将训练集带入优化函数优化\(\theta\)。
注:需要说明的是核函数和相似度函数
核函数:常用的有线性核函数(即没有核函数)和高斯核函数(如下) 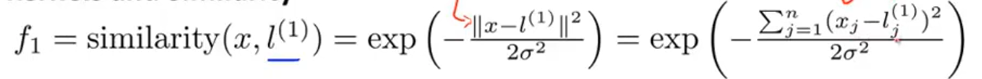 相似度函数:
相似度函数:
\[ h_{\theta}=\theta_{0}+\theta_{1}*f_1+\theta_{2}*f_2+...+\theta_{n}*f_n \]
高斯核函数图像: 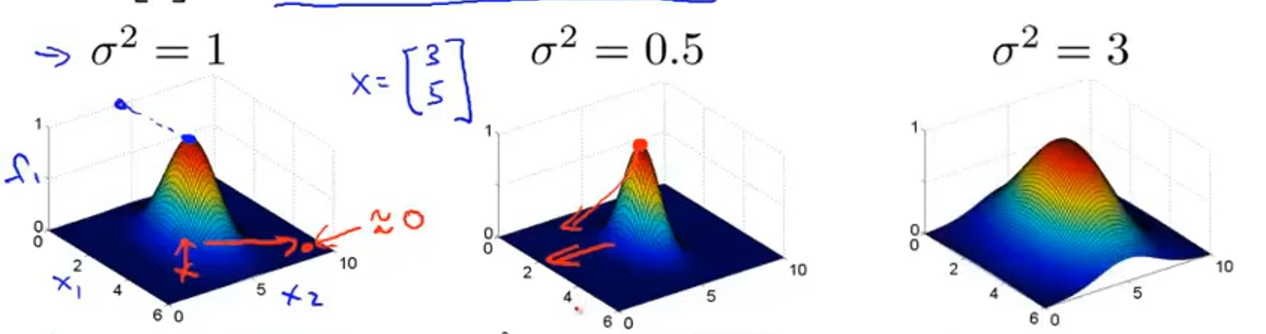 # 优化目标 优化函数为:
# 优化目标 优化函数为: 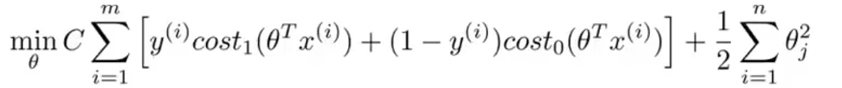
即对于支持向量机的核函数为线性核函数时,分类的决策边界为一条直线,例如:
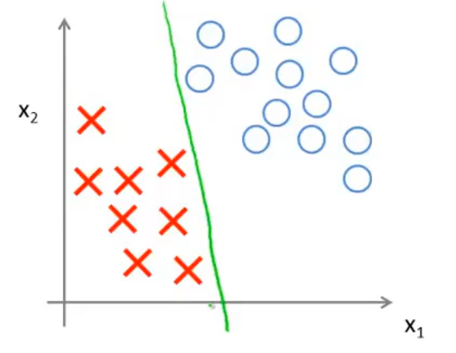
根据优化函数将线性决策边界化为如下黑线所示: 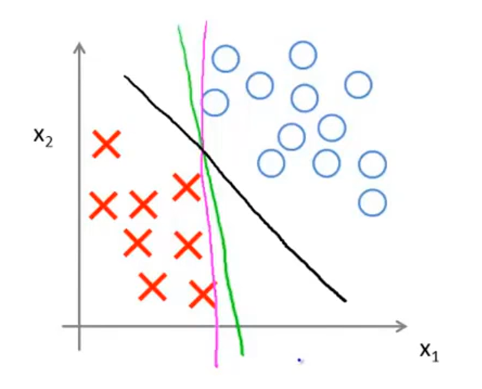
为什么这样优化?详见Andrew Ng的课程
使用高斯核函数
将输入\(x_1\)带入高斯核函数后计算出\(f_i=x_1^Tf_i\),然后将\(f_i\)组合成矩阵f。 判断\(\theta^Tf\)是否大于0,实现分类。
sklearn 实现SVM分类
参考
pluskid
wizardforcel
dongquanc
studyai
scoring参数
1 | import numpy as np |
线性核SVM
1 | %matplotlib notebook |
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object><matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x2300092dd88>1 | x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( |
1.01 | # w0 |
[1.04204619]
[[-0.08757647 0.31572354]]1 | fig = plt.figure() |
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object><mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d.Path3DCollection at 0x23006f8b0c8>高斯核SVM
1 | x, y = make_circles(100, random_state=5) |
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object><matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x23007444088>1 | x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split( |
1.01 | # 若将此处的核函数切换为线性核 |
0.4666666666666667使用玩具数据集iris
1 | iris = load_iris() |
1 | rbfSvc = SVC(C=1, kernel='rbf', gamma=2) |
0.951 | svc = SVC(C=1, kernel='linear') |
0.96666666666666671 | # 使用网格搜索法 |
1 | gv = GridSearchCV(estimator=svc, param_grid=param, cv=5) |
GridSearchCV(cv=5, error_score='raise-deprecating',
estimator=SVC(C=1, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0,
decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3,
gamma='auto_deprecated', kernel='linear',
max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None,
shrinking=True, tol=0.001, verbose=False),
iid='warn', n_jobs=None,
param_grid={'C': [0.5, 1.0, 1.5], 'gamma': [0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0],
'kernel': ['rbf', 'linear']},
pre_dispatch='2*n_jobs', refit=True, return_train_score=False,
scoring=None, verbose=0)1 | print(gv.best_score_) |
0.9866666666666667
{'C': 0.5, 'gamma': 0.5, 'kernel': 'linear'}